Scientific name Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) Synonyms Macrosiphum avenae (Fabriciu3) Homoptera, Polygonaceae. Distribution in the country's wheat production areas.
Host wheat, barley, oats, southern rice, corn, sugar cane, get grass and so on.
Injury characteristics Mai long axillary tube concentrated in the front or back of the leaf, later concentrated in the ear to suck juice, causing the slow growth of the affected strains, reduced tiller, 1000-grain weight drop, is an important pest of wheat crops. It is also a dominant species in wheat bran.
Morphological characteristics Wingless orphan female body length 3,1mm, width 1.4mm, long oval, grass green to orange-red, slightly gray head, ventral grayish green spots. Tentacles, end knots, fiscal festival, belly black. The tail piece is light in color. Abdominal section 6-8 and abdominal mask transverse net pattern, no marginal tumor. In the chest and abdomen short handle. The frontal tumor was significantly extroverted. The antennae are slender, less than full in length, and the basal part of the third section has 1-4 secondary sensory circles. The cockroach is thick and exceeds the base section of the midfoot. The end section is conical, 1.8 times the base width. Abdominal tube is cylindrical in length and is 1/4 in body length. There are more than a dozen lines at the end. The tail piece has a long conical shape and is 1/2 of the length of the ventral tube, with 6-8 curved hairs. The winged female is 3.0mm long, oval, green, and black in tentacles. In the third quarter, there are 8-12 sensory circles lined up. I can't reach the base section of the midfoot. Abdominal tube is cylindrical, black, with 15-16 rows of woven nets at the ends, and a long cone-like tail with 8-9 hairs.
Living habits 20 to 30 generations a year. In most areas, the wingless parthenogenetic nymphs and Rugao live winters in the gaps between the roots of the wheat plant or in the surrounding soil. Some may continue to live on the leeward wheat fields. The worm is incomplete cycle type in central and southern China, that is, the generation of parthenogenetic non-producing crickets is performed throughout the year, and the high-temperature season in summer lived in wheat seedlings or grass weeds in the shaded areas of mountainous areas or high altitudes. In the wheat field, there are two peaks in the spring and fall, and there are fewer summer and winter months. After the emergence of autumn winter wheat, it moved from the summer host to the wheat field for a short period of breeding. A small peak appeared, which was not serious. After mid-to-late November, winter began as the temperature dropped. After returning to spring in spring, the temperature begins to rise above 6°C. The reproduction rate is lower than 15°C, the temperature is higher than 16°C, and the wheat seedlings are transferred to the panicle when heading, and the number of insect fields rises rapidly until the amount of mash during the grouting and milk ripening period reach. At the peak, the temperature is higher than 22°C, producing a large number of winged dragonflies, and moving to cool areas over the summer. The alfalfa in the northern spring wheat region or early sown winter wheat region often produces isolated female and fecundity generations, and two generations of egg generations, alternating generations. In this area more than September moved into the winter wheat field, in early October the average temperature of 14-16 °C into the peak period, the end of September appeared sexual spasm, began spawning in mid-October, in mid-November, the average temperature of 4 °C into spawning During the prosperous period and wintering with this egg. In the middle of March of the following year, the overwintering eggs hatched into a flourishing period and lasted for one month. In the spring, the winter wheat was firstly harmed, and in mid-April, it began to migrate to spring wheat. Whether spring wheat or winter wheat, it reached the peak period of the spike period. In mid-June, a winged plover was again generated and moved to the cool regions where the summer passed. Wheat tuber pods suitable temperature 10 to 30 °C, of ​​which 18-23 °C optimum, the temperature of 12-23 °C calving 48-50 head, 24 °C then decreased. The main natural enemies include ladybugs, hoverfly, grasshoppers, spiders, apes, and molds.
Prevention Methods (1) Forecasting. When the panicle planting rate reaches 50%, 100 plants have 200-250 average alfalfa or 70% alfalfa plants at the initial stage of alfalfa, and 100 plants have 500 alfalfa averages. (2) Agricultural Control Law 1 Selection of insect-resistant varieties. Such as: "Lumai 23". 8 rational layout. Winter wheat mixed area, to minimize the area of ​​winter wheat or winter wheat and spring wheat were planted separately, so as to reduce the damage. 8 timely sowing. Appropriate late sowing of winter wheat, early spring sowing timely. 4 Reasonably apply fertilizer and water. (3) Biological control Reduce or improve the application of pesticides to avoid killing natural enemies in wheat fields. Using natural enemies such as ladybugs, hover flies, grasshoppers, and cockroaches and bees, it has been determined that adults of coccinella septempunctata, more than 100 eels of eclipses, and the equivalent system of wheat cockroaches composite natural enemies can be used in production to unify the standards of various natural enemies. The restaurant units and calculation methods used to accurately determine the comprehensive control capacity of composite natural enemies were based on other measures. The index of the control of natural enemies is measured, and this index is combined with chemical defense indicators and equivalent systems to provide guarantees for the full use of natural enemies. If necessary, it can be artificially propagated to release or assist natural enemies; it can effectively control locusts. When the enemy is unable to control the wheat bran, use 0,2% matrine (Ketzebolin) 400 times solution or chlortetracycline (spore content 2 million pieces/ml) 250 times, 50% or more. 40% Omethoate 2000 times, 90% kill effect, and can protect natural enemies. (4) The following comprehensive prevention measures may be adopted in areas or fields where the above measures do not work. 1 In the wheat yellow dwarf epidemic area, the disease is mainly treated at the seedling stage, using 0.3% of 75% 3911 EC, adding about 7% of the amount of fresh water, sprayed on the wheat seed, and stirring while spraying. It is also possible to use 50% chlorinated pine oil 150ml, 5kg of water, spray on 50kg of wheat, and soak for 6-12 hours. 8 With 3% carbofuran granules or 5% aldicarb granules, 5% 3911 granules, 1.5kg caps per 667m2, the effective period of up to 1-1.5 months. 2 During the epidemic period of non-yellow dwarf disease, wheat stubble should be controlled at the ear stage, if necessary, spraying 2.5% Hutuo WP or 10% imidacloprid (one-time-net) wettable powder 2500 times or 2.5% high-immunity imidacloprid wettable. Powder 3000 times solution, 50% anti-inferiority WP 3500-4000 times, 18% hypertonic omethoate EC 1500 times, 50% malathion EC 1000 times, 20% Confodol Solvent Or 90% of Acrylic Soluble Powder 3000-4000 times, 50% of Acetate Loose Emulsion 2000 times or 2.5% of deltamethrin EC 3000 times. 40% Huifeng No.1 EC can also be used, 30mL per 667m2, water 40kg, 99% efficiency, better than 40% omethoate. 4 40% of Dimethoate EC 50ml can be used per 667m2 in arid regions, 1-2kg for water, 15kg fine sandy soil, or 80% dichlorvos EC 75ml, and 25kg for soil mixing. The wheat can be withdrawn early in the morning or in the evening. In order to protect natural enemies, we choose to use pesticides such as anti-vigilance that have little lethal effect on natural enemies. 5 When wheat bran and powdery mildew are mixed together, spraying 11% of oleocalin EC 100ml, 50kg of water, the effect of controlling wheat bran is the same as that of omethoate, and the effect of controlling powdery mildew is equivalent to that of triadimefon. 8 Try 20% dichlorvos heavy smoke agent 9-10.5kg/hm2, smoke 0.5 hours later, the smoke gradually settled on the crop, control efficiency of about 80%.
T-Fiberglass Beams is our company's high-quality livestock used slat flooring system support equipment, which is a kind of Fiberglass Beams, it looks like the letter "T" from the side. Made of a special antifreeze, high temperature material, ranging in size from 110mm to 120mm, with ruggedized features. T-fiberglass Beams installation and use of very convenient, is a very good agricultural farming equipment. We can produce according to your special requirements, can also be produced according to your drawings. Our commitment to our products, our T-fiberglass beams are of high quality and easy to use. Looking forward to your patronage.
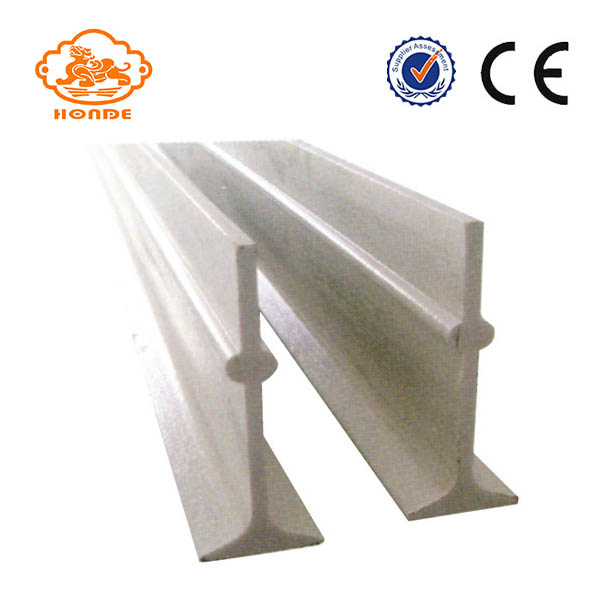
T-fiberglass Beams
T-Fiberglass Beams,Durable T-Fiberglass Beam,T-Fiberglass Beam For Farrowing Crates,Strong T-Fiberglass Beam
HuangHua FengYi Honde Metal Factory , https://www.farrowingcratesfromchina.com